Disease management : Anthracnose
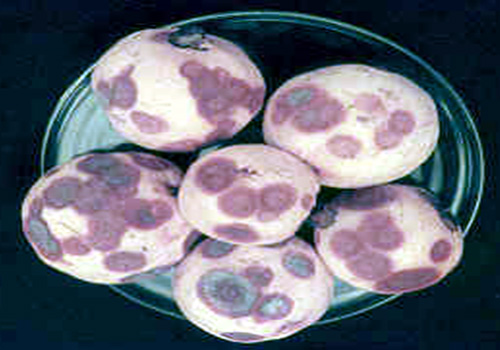
 Symptoms:
Anthracnose is manifested in
symptoms as die-back, twig blight, wither tip and fruit spot. On
the unripe fruits small, dark brown, sunken and small spots of
pin head size are observed. These spots gradually enlarge to 5 –
6 mm in diameter; coalesce to form a corky hard lesion having
cracks. The ripe fruits become soft and at times drop off.
Unopened buds and flowers are also shed. Foliage develops
necrotic gray lesion at tips and margins. Tender branches dry
from tip downward exhibiting ‘die back’. The growing tips of the
branches die and necrotic and dead areas spread downwards. The
leaves, flowers and fruits are sh3ed and unripe fruits remained
mummified. Fruits carry the incipient infection from the field
that manifests itself in storage causing rotting of fruits.
Symptoms:
Anthracnose is manifested in
symptoms as die-back, twig blight, wither tip and fruit spot. On
the unripe fruits small, dark brown, sunken and small spots of
pin head size are observed. These spots gradually enlarge to 5 –
6 mm in diameter; coalesce to form a corky hard lesion having
cracks. The ripe fruits become soft and at times drop off.
Unopened buds and flowers are also shed. Foliage develops
necrotic gray lesion at tips and margins. Tender branches dry
from tip downward exhibiting ‘die back’. The growing tips of the
branches die and necrotic and dead areas spread downwards. The
leaves, flowers and fruits are sh3ed and unripe fruits remained
mummified. Fruits carry the incipient infection from the field
that manifests itself in storage causing rotting of fruits.
Epidemiology:
The disease is mostly favoured by
high humidity. During moist weather profuse production of
acervuli is noticed on dead parts of twigs and the spores come
out as a pinkish mass. These are further disseminated by rain or
wind and cause fresh infection. The disease develops more
rapidly on the ripe fruits and maximum spreads takes place at 30
°C and relative humidity of 96%.
Management:
Sprayings of Bordeaux mixture (3:3:50) or
Copper oxychloride (Blitox 0.2%) at weekly intervals starting
from the month of July manage the disease. Among systemic
fungicides Carbendazim (Bavistin 0.1%) or Thiophanate methyl
(Topsin M or Roko 0.1%) provide effective disease control.