Guava Crop Management
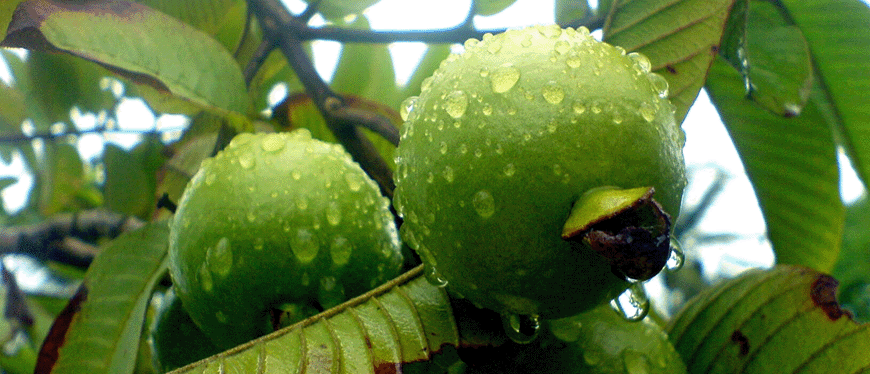
Guava (Psidium guajava) : Guava grows on small trees with spreading branches, may grow to a height and spread of 6-9 m. Guava trees produce white, 1-inch flowers that yield to small round, oval or pear shaped fruits. They have soft flesh, which may be white, pink, or red depending on variety. The skin is edible. The guava bears fruit all year round. Guava trees grow well in tropical conditions, though it can tolerate drought better than many tropical fruits. It is also adapted to many soil types and may thrive even on shallow, infertile soils. Green when unripe but some cultivars will stay light green even when it is ripe and some will turn yellow.
Diagnostic Solutions
-
 Disease
management
The important diseases of
guava are wilt, anthracnose, die back, canker, fruit
rot, and dry rot, Styler end rot and seedling
blight
Disease
management
The important diseases of
guava are wilt, anthracnose, die back, canker, fruit
rot, and dry rot, Styler end rot and seedling
blight
-
 Pest
Management
The insect pest mostly seen are fruit
fly, green shield scale, Mirid bug, Mealy bug, Bark
eating cater pillar and tea musquito bug.
Pest
Management
The insect pest mostly seen are fruit
fly, green shield scale, Mirid bug, Mealy bug, Bark
eating cater pillar and tea musquito bug. -
 IIHR Varieties:
The IIHR released varieties are Arka Mridula, Arka
Kiran, Arka Reshmi and Arka Amulya.
IIHR Varieties:
The IIHR released varieties are Arka Mridula, Arka
Kiran, Arka Reshmi and Arka Amulya.
Technologies
Guava fruit is highly perishable in nature and needs value adddition. Traditionally guava is processed into various products such as Jelly, Juice, Fruit bar, etc. A pre treatment, such as osmotic dehydration can be used in order to reduce the initial water content, reducing total processing and air drying time.